Parameters for Reporting Fuel Energy Use and CO2 Emissions
In the Protocol Spreadsheet the energy and CO2 emissions from fuel use are reported based on the data of the fuel consumption, lower heating values (LHV![]() Lower heat value), and the matching CO2 emission factors (EF
Lower heat value), and the matching CO2 emission factors (EF![]() Emission factor):
Emission factor):
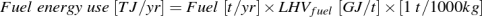
where:
- Fuel = Amount of fuel in tonne per year
- LHVfuel = Lower heating value of fuel in gigajoules per tonne
Equation 13: CO2 emissions from fuels
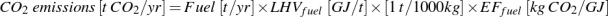
where:
- Fuel = Amount of fuel in tonne per year
- LHVfuel = Lower heating value of fuel in gigajoules per tonne
- EFfuel = Emission factor of fuel in kg CO2 per gigajoule
Lower Heating Value (LHV)
Fuel consumption and lower heating values (LHV or net calorific value NCV) of fuels are routinely measured at plant level.
It is important to note that the applied heating value always has to match the status of the fuel, especially with respect to the correct moisture content.
Fuels might have variable moisture content during its weighing (e.g. raw coal or dried coal). Normally the lower heating value (LHV![]() Lower heat value or net calorific value NCV
Lower heat value or net calorific value NCV![]() Net calorific value) is determined from a dried sample. Subsequently a moisture correction has to be applied to the results, e.g. by correcting the mass reference of the LHV
Net calorific value) is determined from a dried sample. Subsequently a moisture correction has to be applied to the results, e.g. by correcting the mass reference of the LHV![]() Lower heat value from the dried sample back to the original moisture content of the fuel as it is consumed or weighed (e.g. for raw coal and dried coal).
Lower heat value from the dried sample back to the original moisture content of the fuel as it is consumed or weighed (e.g. for raw coal and dried coal).
Furthermore, the correct reference of the CO2 emission factors (EF) must be assured. The reference should be to the heat determined by the lower heating value (LHV).
For the conversion of higher heating values (HHV![]() Higher heat value or gross calorific value GCV
Higher heat value or gross calorific value GCV![]() Gross calorific value) to LHV the equation defined in the 2006 IPCC Guidelines (Vol. II, Section 1.4.1.2, Box 1.1) can be applied (see Lower and Higher Heating Values (LHV and HHV)).
Gross calorific value) to LHV the equation defined in the 2006 IPCC Guidelines (Vol. II, Section 1.4.1.2, Box 1.1) can be applied (see Lower and Higher Heating Values (LHV and HHV)).
Generally, the CO2 emission factors of all fuels should represent the complete CO2 emissions from the use of the fuel based on the total carbon content (TC). Due to very high combustion temperatures in cement kilns and the long residence time in kilns, carbon in all kiln fuels shall be treated as fully oxidized.
Companies are encouraged to use plant- or country-specific emission factors if reliable data are available. Alternatively, IPCC and CSI Cement CO2 and Energy Protocol default emission factors per GJ lower heating value are listed in the Fuel CO2 Factors Sheet and the
List of Constants and Default CO2 emission factors
. However, the CO2 emission factors of alternative fuels (AF![]() Alternative fuels) and mixed fuels depend very much on the type of fuel and, therefore, should be specified at plant level where practical.
Alternative fuels) and mixed fuels depend very much on the type of fuel and, therefore, should be specified at plant level where practical.
CO2 emission factors (per lower heating value in [kg CO2/GJ]) for kiln fuels and non-kiln fuels are reported in line186 to line209.
Biogenic carbon content (Cbio/TC) of mixed fuels
CO2 from biomass fuels and the biogenic carbon content of mixed fuels is considered climate-neutral, because biogenic CO2 emissions can be compensated by the re-growth of biomass in the short term. According to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines CO2 from the combustion of biomass (including biomass fuels, biomass wastes and the biomass fraction of mixed fuels) is therefore reported separately as a "memo item", but excluded from the total direct CO2 emissions.
Consequently, the CO2 emissions of Mixed fuels![]() Term used in this Guidance Document for referring to fuels that are a mix of
biomass and fossil fuel, i.e. fuel with a certain biogenic carbon content. shall be separated in their fossil and biogenic part. This is done by determining the share of the biogenic carbon in the fuel's overall carbon content, according to international standards (e.g. EN 15440).
Term used in this Guidance Document for referring to fuels that are a mix of
biomass and fossil fuel, i.e. fuel with a certain biogenic carbon content. shall be separated in their fossil and biogenic part. This is done by determining the share of the biogenic carbon in the fuel's overall carbon content, according to international standards (e.g. EN 15440).
Companies are advised to use a conservative approach in determining the biogenic carbon content, meaning that the biogenic carbon content should not be overestimated. A fossil carbon content of 100% should be assumed for fuel types in the case of a lack of reliable information on their biogenic carbon content until more precise data becomes available.
The biogenic carbon contents (Cbio) per total carbon content (TC) of mixed fuels are reported in line200a to line200h. Please use a value of 0% if the fuel does not contain biogenic carbon and is therefore a purely fossil fuel or if the biogenic carbon content is very uncertain or unknown.
Equation 14: Biomass CO2 emissions (Memo Item)
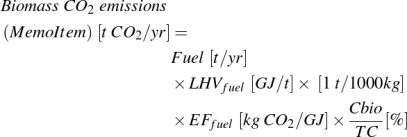
where:
- Fuel = Amount of fuel in tonne per year
- LHVfuel = Lower heating value of fuel in gigajoules per tonne
- EFfuel = Emission factor of fuel in kg CO2 per gigajoule
- Cbio/TC = Percentage of biogenic carbon content
Fossil carbon content of mixed fuels
Direct CO2 from the combustion of fossil fuels, fossil alternative fuel and the Fossil carbon![]() Carbon derived from fossil fuel or other fossil source.
Definition taken from: Glossary of the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories fraction of mixed fuels should be calculated and included in the direct CO2 emissions:
Carbon derived from fossil fuel or other fossil source.
Definition taken from: Glossary of the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories fraction of mixed fuels should be calculated and included in the direct CO2 emissions:
Equation 15: Direct fossil CO2 emissions
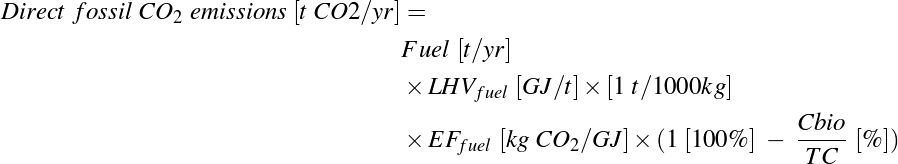
where:
- Fuel = Amount of fuel in tonne per year
- LHVfuel = Lower heating value of fuel in gigajoules per tonne
- EFfuel = Emission factor of fuel in kg CO2 per gigajoule
- Cbio/TC = Percentage of biogenic carbon content
The Protocol Guidance Document (Chapters 3.5, 3.6 and 5) provides more detailed guidance for reporting CO2 from conventional fossil fuels, alternative fuels, mixed fuels and biomass fuels.